Interoperability – The core tool to execute Karkinos’ democratized cancer care service
By Kumar Satyam, Deputy Chief Product Officer, Karkinos Healthcare
Karkinos Healthcare is on a mission to make the best oncology care accessible to anyone who needs it from anywhere. The company is dedicated to delivering the 4Ds: Detection, Diagnosis, Delivery, and Data in cancer care. Apart from the intention to offer democratized and distributed cancer care services in a participatory manner, Karkinos Healthcare is working to develop a Phygital Metaverse for Oncology, in which patients receive the best possible care and direction from care experts stationed anywhere on the planet, either through digital mediums or in physical care centers, closer to their homes.
A phygital (physical + digital) metaverse enables detection, diagnosis and delivery of healthcare services over a hybrid medium made possible through Artificial Intelligence (AI), Virtual Reality (VR), Augmented Reality (AR), blockchain, imaging and other existing and emerging digital technologies. Healthcare metaverse makes physical boundaries disappear. This kind of an environment breaks walls and ceilings that limit healthcare services, establishes a connection, and bridges the gaps between care seekers and care providers. Not only that, the cost incurred by both the parties is substantially reduced with healthcare services delivered over a phygital environment.
Let me tell you that the metaverse mentioned here is not some sci-fi fantasy prediction for the far-off future. It’s happening today, at this moment! Global as well as Indian health-tech enthusiasts are already building its foundation blocks. It is possible to create a digital twin of a person/patient. Longitudinal health records using data from medical records, wearables & various sensors on IoMT are being created with ease. Virtual care teams, AI assistants, digital real-time payer-provider collaboration, telemedicine, healthcare data platforms exist today and they are improving at a rapid pace. With all these in place, healthcare becomes readily accessible at the patient’s location (where the patient need not move, but the patient’s health data moves).
While to do that, electronically recording patient data becomes the crux, and using the data to make treatment options better and cost effective has become the need of the hour.
This way of handling patient data has led to the global awakening of reaping the benefits of interoperability in healthcare. Interconnected, interoperable systems are the backbone on which the metaverse is built.
Likewise, interoperability is core to the Karkinos’ cancer care network. Why and how is what I have discussed in detail in this blog and will be delving more on the advantages of interoperability in the forthcoming ones.
Defining interoperability
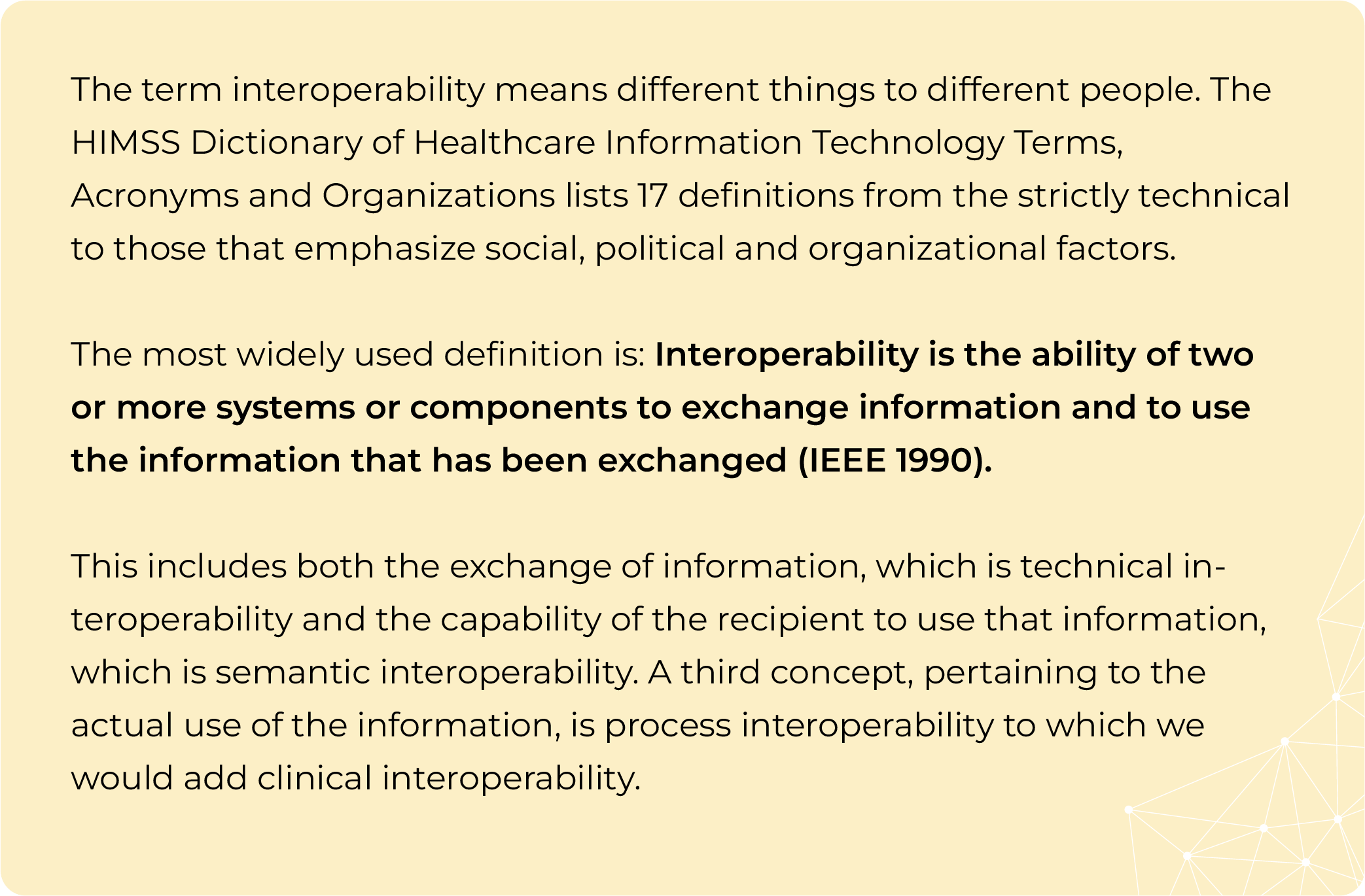
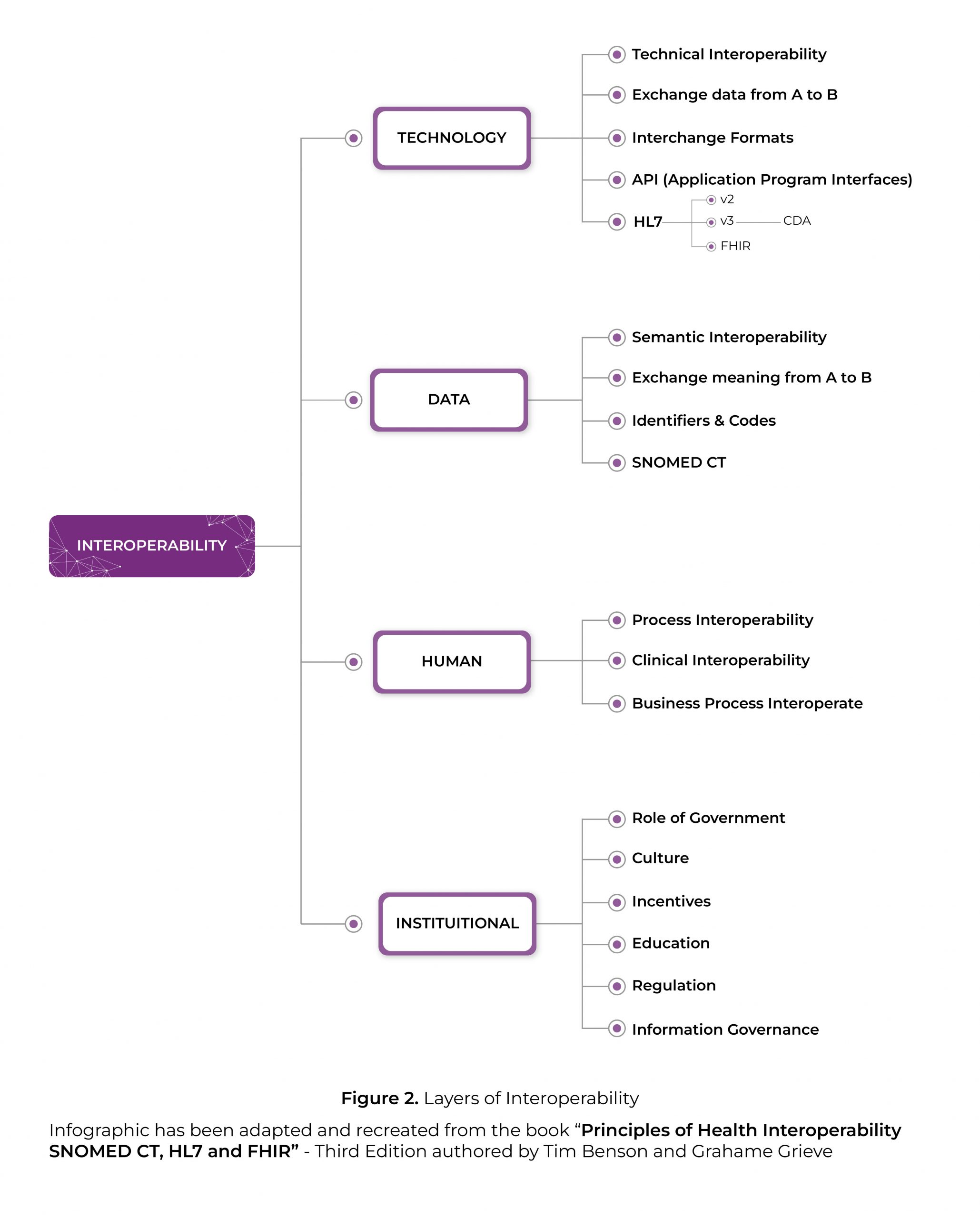
Tim Benson and Grahame Grieve in their co-authored book on ‘Principles of Health Interoperability’ say the task of interoperability is to deliver the right information at the right time to the right place. Everybody (patient, clinician, manager and payer) stands to benefit from more soundly based decisions, safer care and less waste, errors, delays and duplication. Going by that principle, interoperability can be defined as the ability for healthcare technology systems and devices to exchange, interpret, and store data using common standards.

Making patient data available more securely through interoperability
Computer science has helped us come quite far with storing health data electronically. Information Technology has furthered this into developing data exchange platforms that can be extensively leveraged for the benefit of both the care provider as well as the care receiver. We live in the era of modern healthcare that is distributed, multi-disciplinary, multi-party and continuous. So, health data exchange architectures, application interfaces (APIs), and standards were developed to enable data to be accessed and shared appropriately and securely across a complete spectrum of care, within all applicable settings and with relevant stakeholders, including the patient.
During one’s lifetime, a person visits many healthcare facilities and doctors. Each encounter creates new health data, which is documented and maintained as different files either with the patient or with the facility. In most cases, it is usually the patient’s responsibility to maintain his/her medical records. Similarly, vital patient health information would be locked at one or more facilities of care, resulting in fragmented health information that may not be available in a comprehensive format when needed. Interoperability, on the other hand, transforms this fragmented & siloed health information into a federated and longitudinal health record of the person.
In simple terms, interoperability refers to the basic ability of computerized systems to connect and communicate with one another readily to make patient data easily available. And, it also refers to timely and secure access, integration, and use of electronic health data so that it can be used to optimize health outcomes for individuals and populations. Being able to exchange information between applications, databases, and other computer systems is considered crucial for the future of the healthcare industry.
Interoperability, therefore, describes the extent to which systems and devices can exchange data, and interpret that shared data. For two systems to be interoperable, they must be able to exchange data and subsequently present that data such that it can be understood for clinical decision making.
Widespread implementation of interoperability will ultimately strengthen the public healthcare system by making it more proficient in disseminating proactive solutions. For example, during the Covid-19 pandemic, healthcare providers and several government backed portals displayed real-time ICU bed availability at a desired locality’s healthcare facilities. Such publicly available real-time data came to several people’s rescue at a time of great crisis. In the long run, effective deployment of interoperability would have collectively benefitted in strengthening the Public Health Systems of a country.
Also, health data needs to facilitate clear, concise and contextual information for effective communication and teamwork. Today healthcare is facing data deluge, volume of data is on the rise from existing, new and expanding sources of data. Sifting through this data pile and finding relevant information at the time of need is challenging. Interoperability does good by clearing messy and ambiguous data into meaningful information that helps clinicians make informed decisions.
A person’s health history is made up of several episodes of care in different care settings. Data from different sources need to come together and fit in seamlessly into one health record for a person. The ultimate long-term goal of interoperability is to create a unified health record that gets constantly updated with new data from multiple sources instantaneously.
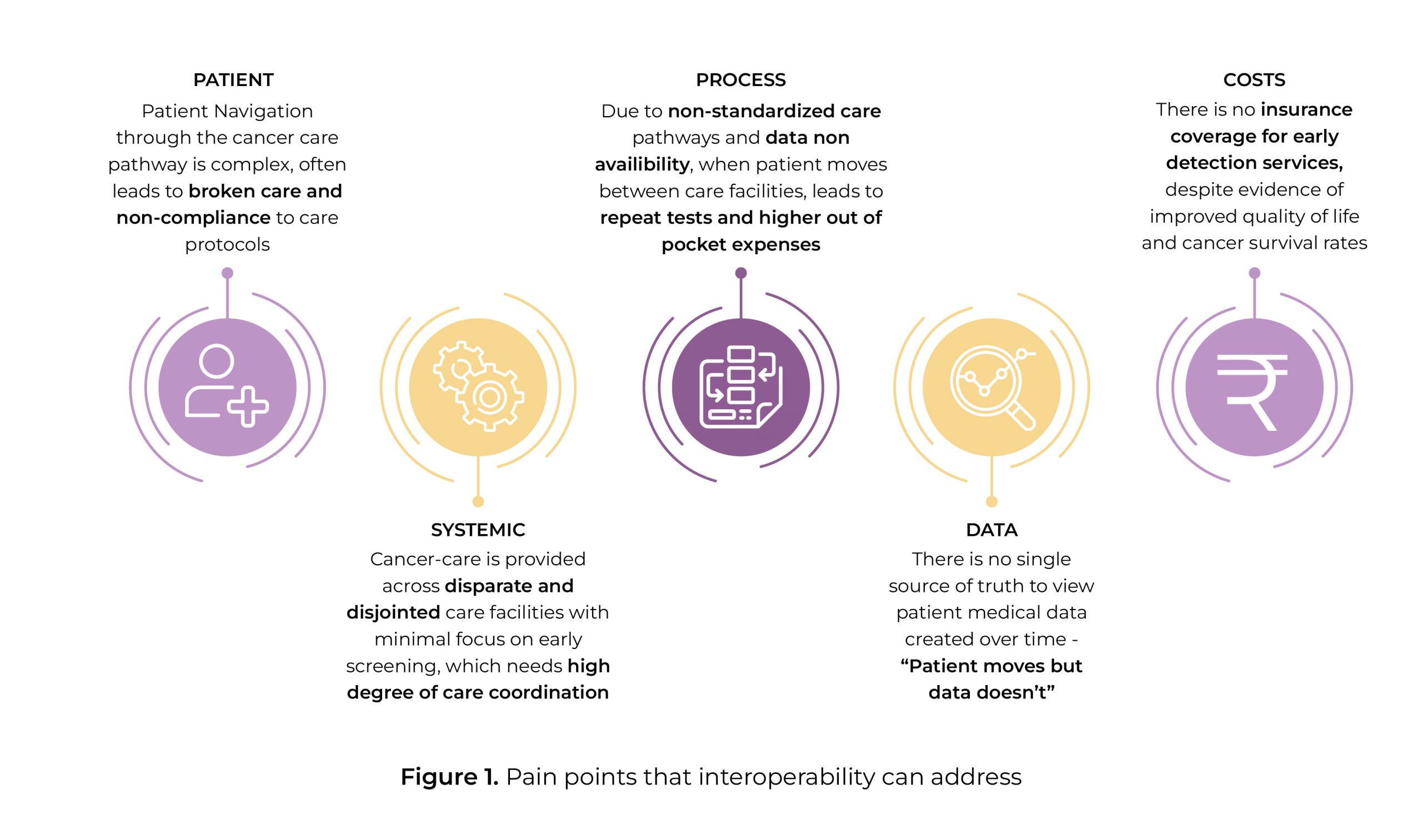
Interoperability has several other advantages. To name a few, one’s entire health information is at their disposal, and they can share it with anyone they wish. They have control over what data is exchanged and what the recipient can do with it. They have access to the best care, irrespective of where they are and at the most competitive price. Clinicians have access to every relevant detail that they need to perform their task irrespective whether they are treating an individual or a population. Duplication of diagnostic tests that are expensive can definitely be overcome with interoperability.
In addition to helping physicians and other healthcare providers see a more complete view of their patients, health data interoperability helps organizations across the entire healthcare industry. If health information systems were more integrated, then health plans would be able to develop a better understanding of their utilization rates and demand for services. Clinical research, policy formulation or claims reimbursement everything is much more efficient with interoperability in place.
Interoperability, thus, provides value to every stakeholder in the health ecosystem. The following infographic outlines some benefits of interoperability to the stakeholders in the healthcare ecosystem.
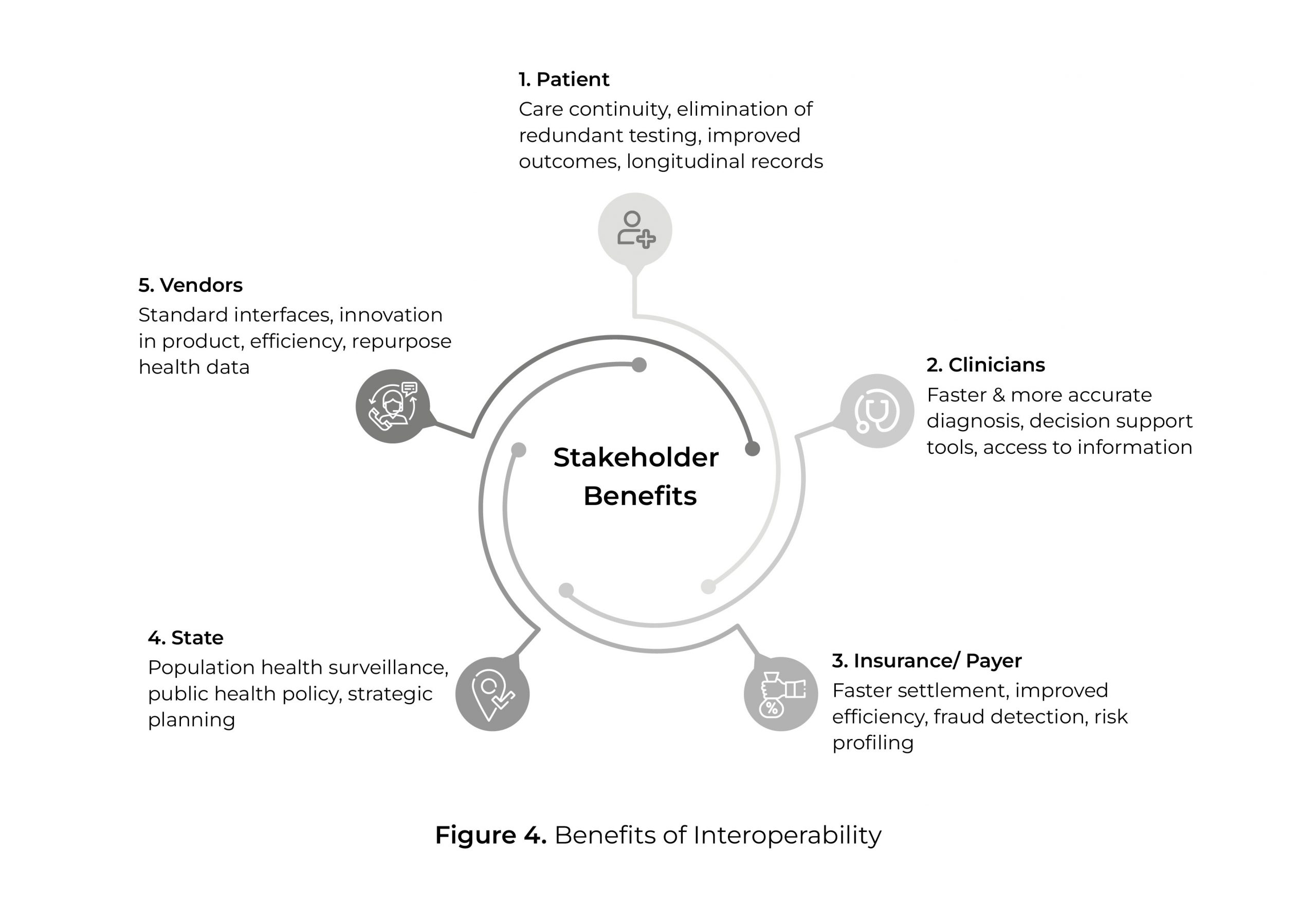
Executing Karkinos’ mission and vision with interoperability
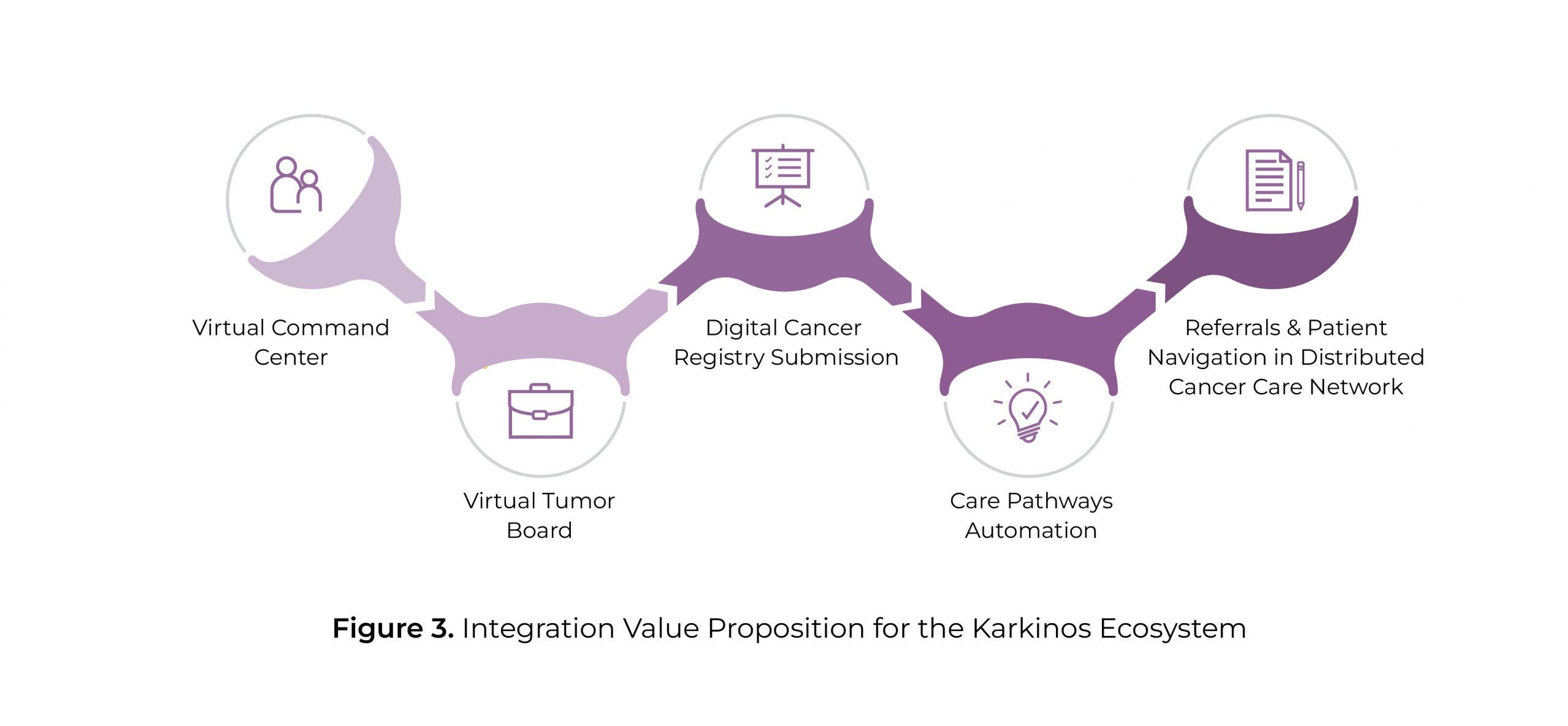
Karkinos Healthcare’s intention is to significantly enhance access to cancer care services by creating a technology enabled data-driven platform wherein the knowledge architecture is centralized, and the delivery systems are democratized and distributed. In order to achieve these, the company has conceived a ‘hub-and-spoke and further spoke’ model backed by a robust technology and clinical decision support systems.
The model, therefore, relies on a technology backbone that enables anchor referral hospital/s that cater to complex cases, surgery, and radiotherapy be supported by a network of smaller cancer centers that offer diagnosis and basic treatment. Hence, we bring about a decentralized approach to care and also reduce the load on Apex centers for non-complex treatment while increasing accessibility and cutting down on loss of productive days for the family. The network is designed to be ‘wired’ to enable connectivity amongst all centers, seamless access to data, diagnostics, and patient consulting – which includes a combination of a central knowledge repository, diagnostic capabilities, and a continuous care.
With interoperability playing at our advantage, the concept so far is yet to be completely utilized. Its advantages are plenty and scores a huge plus in scaling healthcare IT operations for the benefit of the entire fraternity and its stakeholders.
So, as soon as a patient enters into the Karkinos Healthcare’s ecosystem, the patient information is digitally recorded and exchanged, and all interactions thereafter are managed through the platform. Patient registration, referrals, service requests, diagnostics and treatment related, prescriptions, clinical summaries are all exchanged digitally and in real time.
In addition, data received from different patient touch points like vitals recorded by mhealth apps, sensors, wearables, remote patient monitoring devices and applications need clinician’s attention. Referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT), data from several such sources of modern medical interventions are crucial for a 360 degree care approach.
Data is just not limited to clinical encounters. Non-clinical patient information such as a patient’s social profile, demographics, family history of diseases, etc. need to be incorporated into the patient’s health record. There is also data from genomic testing, risk assessment, and other health parameters. To get all this into seamless action, interoperability, therefore, has to be enabled, ensuring that the longitudinal data record is neatly stitched to make an entire paradigm of care truly a success.
Leveraging interoperability’s features is going to be Karkinos Healthcare’s ingrained task. The company is very clear, from its early inception days, to provide end-to-end cancer care service.
End-to-end service refers to the healthcare service provider taking charge of an individual’s health right from screening, diagnosis, through the different stages of treatment and finally until the patient is healed or up to the palliative care stage.
The care can be delivered to the patient at a hospice or even at the patient’s home or any convenient location. Remember, be it in hospice care or at the patient’s home, every patient encounter results in medical data generation that needs to be recorded safely for successful clinical knowledge, decisions, and actions.
This holistic form of health data should be made available at any point of time to enable care continuum for the patient and all these requirements can be vested easily on secure, interoperable systems that provisions data exchange seamlessly. Health records can, thus, be securely shared with patients and other clinicians and health care settings to enable coordinated patient care.
Karkinos Healthcare’s platform natively supports major healthcare data exchange standards like HL7 V2.x, HL7 FHIR, DICOM, IHE and terminology standards like SNOMED, LOINC, ICD. The platform supports all exchange paradigms like REST, messaging, documents and services. The platform is hybrid, which enables us to seamlessly integrate with both on-premise and cloud systems. Karkinos Healthcare’s platform adheres and supports security and privacy best practices. We guarantee a reliable, secure, flexible and seamless data exchange within the Karkinos Healthcare’s partner ecosystem. Every record passing through the Karkinos’ platform is fully auditable.
The Command Center is another major strength of Karkinos Healthcare, which is central to the hub-and-spoke model of cancer care. It maps the entire patient journey at Karkinos across the care network. The command center’s main objective is to help connect patients to a care facility closest to their homes. To fulfill this requirement, Karkinos Healthcare partners with different types of care providers who can deliver cost-effective, affordable cancer care to the needy. While to do this, data exchange is utmost important. Interoperability makes this data exchange possible over a secure environment. When partner hospitals come into the fold of Karkinos Healthcare’s network, interoperability by default gets translated into the respective hospital’s functioning.
With interoperability playing at our advantage, the concept so far is yet to be completely utilized. Its advantages are plenty and scores a huge advantage in scaling healthcare IT operations for the benefit of the entire fraternity and its stakeholders.
As Karkinos Healthcare works towards its mission of delivering accessible and affordable cancer care, interoperability will peg to offer a pillar of strength to its undeterred efforts and support the company’s operations in the healthcare metaverse.
This blog serves as an introduction to Karkinos Healthcare’s efforts to capitalize on interoperability. In the coming blogs, I’ll go into the nuances of the concept and Karkinos Healthcare’s approach to interoperability.
Stay Tuned!

 About Kumar Satyam
About Kumar Satyam